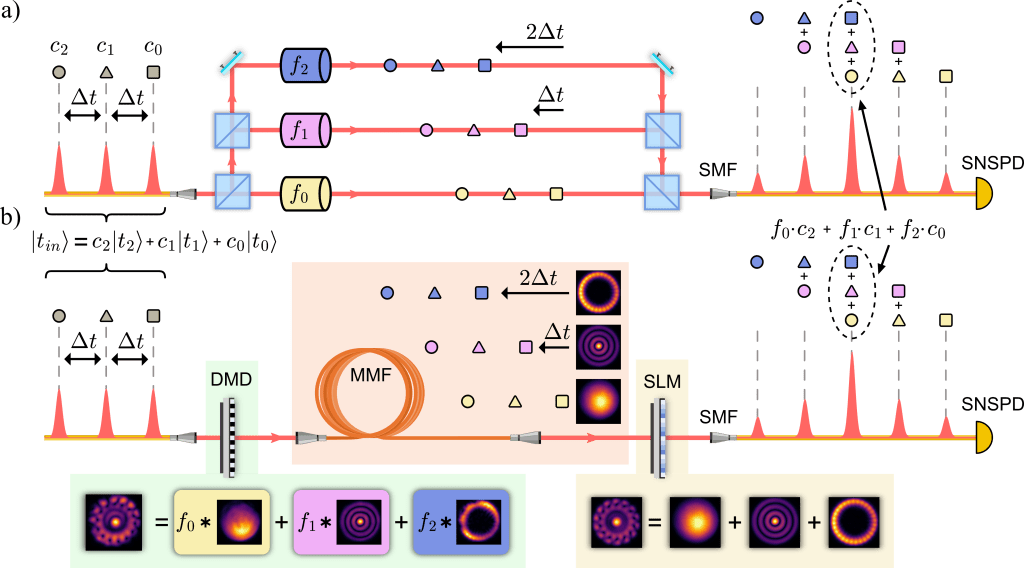
In our recent review, published in Advanced Photonics, we examine how spatially structured light—in which the shape and mode structure of photons are precisely engineered—is opening powerful new directions in quantum information science.
Rather than restricting information to simple two-level qubits, we highlight how photons can be prepared in high-dimensional quantum states (qudits) by encoding information in their transverse spatial degrees of freedom. This approach dramatically expands the information capacity of a single photon, enabling richer correlations, stronger noise resilience, and more efficient communication protocols.
Crucially, spatial modes are highly programmable. Using top-down optical circuit platforms—such as multi-plane light converters—researchers can implement complex, high-dimensional transformations in compact and scalable architectures. This makes advanced functionalities, including multi-party operations and multi-outcome measurements, directly accessible within a single optical system.